Set Ball Position
We set the ball into a fixed position on the screen by passing in coordinates
Published
Liked the article? Share it!
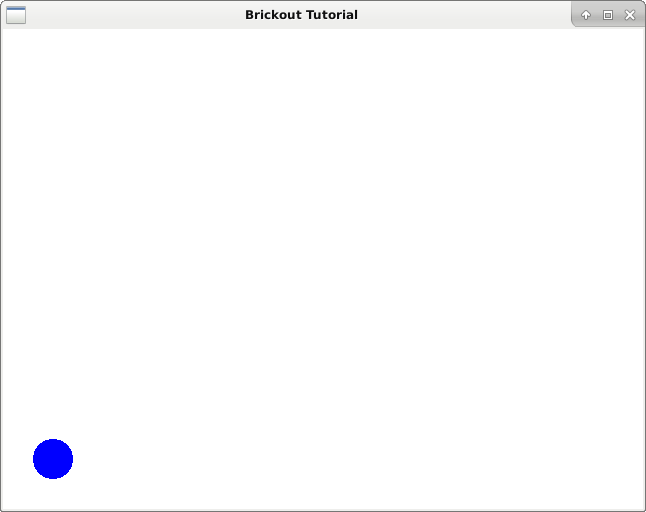
A common technique that you will become familiar with in OpenGL is having your assets with local coordinates at the origin. These assets are then positioned into the scene where you need with a model position (mvp) matrix. To do this, we’ll edit our vertex shader again.
Vertex Shader
shader/vertex.glsl
#version 120
uniform mat4 mvp;
uniform mat4 orthograph;
attribute vec2 coord2d;
void main (void) {
vec4 pixel_pos = mvp * vec4(coord2d, 0.0, 1.0);
gl_Position = orthograph * pixel_pos;
}
Main Program
Next we’ll add the mvp matrix into our main program.
main.c
#include <epoxy/gl.h>
#include <epoxy/glx.h>
#include <gtk/gtk.h>
#include <math.h>
#include "DashGL/dashgl.h"
#define WIDTH 640.0f
#define HEIGHT 480.0f
static void on_realize(GtkGLArea *area);
static void on_render(GtkGLArea *area, GdkGLContext *context);
GLuint program;
GLuint vao, vbo_circle;
GLint attribute_coord2d;
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
GtkWidget *window;
GtkWidget *glArea;
gtk_init(&argc, &argv);
// Initialize Window
window = gtk_window_new(GTK_WINDOW_TOPLEVEL);
gtk_window_set_title(GTK_WINDOW(window), "Brickout Tutorial");
gtk_window_set_position(GTK_WINDOW(window), GTK_WIN_POS_CENTER);
gtk_window_set_default_size(GTK_WINDOW(window), 640, 480);
gtk_window_set_type_hint(GTK_WINDOW(window), GDK_WINDOW_TYPE_HINT_UTILITY);
g_signal_connect(window, "destroy", G_CALLBACK(gtk_main_quit), NULL);
// Initialize GTK GL Area
glArea = gtk_gl_area_new();
gtk_widget_set_vexpand(glArea, TRUE);
gtk_widget_set_hexpand(glArea, TRUE);
g_signal_connect(glArea, "realize", G_CALLBACK(on_realize), NULL);
g_signal_connect(glArea, "render", G_CALLBACK(on_render), NULL);
gtk_container_add(GTK_CONTAINER(window), glArea);
// Show widgets
gtk_widget_show_all(window);
gtk_main();
return 0;
}
static void on_realize(GtkGLArea *area) {
// Debug Message
g_print("on realize\n");
gtk_gl_area_make_current(area);
if(gtk_gl_area_get_error(area) != NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, "Unknown error\n");
return;
}
const GLubyte *renderer = glGetString(GL_RENDER);
const GLubyte *version = glGetString(GL_VERSION);
const GLubyte *shader = glGetString(GL_SHADING_LANGUAGE_VERSION);
printf("Shader %s\n", shader);
printf("Renderer: %s\n", renderer);
printf("OpenGL version supported %s\n", version);
glClearColor(1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f);
glGenVertexArrays(1, &vao);
glBindVertexArray(vao);
int i;
float angle, nextAngle;
int num_segments = 100;
GLfloat circle_vertices[6 * 100];
for(i = 0; i vec3 pos = { 50.0f, 50.0f, 0.0f };
mat4 mvp;
mat4_translate(pos, mvp);
glUniformMatrix4fv(uniform_mvp, 1, GL_FALSE, mvp);
}
static void on_render(GtkGLArea *area, GdkGLContext *context) {
g_print("on render\n");
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT);
glBindVertexArray(vao);
glEnableVertexAttribArray(attribute_coord2d);
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, vbo_circle);
glVertexAttribPointer(
attribute_coord2d,
2,
GL_FLOAT,
GL_FALSE,
0,
0
);
glDrawArrays(GL_TRIANGLES, 0, 3 * 100);
glDisableVertexAttribArray(attribute_coord2d);
}
Compile
$ gcc -c -o DashGL/dashgl.o DashGL/dashgl.c -lepoxy -lpng -lm
$ gcc `pkg-config --cflags gtk+-3.0` main.c DashGL/dashgl.o `pkg-config --libs gtk+-3.0` \
-lepoxy -lm -lpngRun
$ ./a.out